QR – short for Quick Response codes, have the ability to store a large amount of data. QR codes have become omnipresent in modern life. They are found in every modern retail institution, on the back of a business card and have become ubiquitous recently among the street vendors as a payment solution.
What does a QR Code look like?
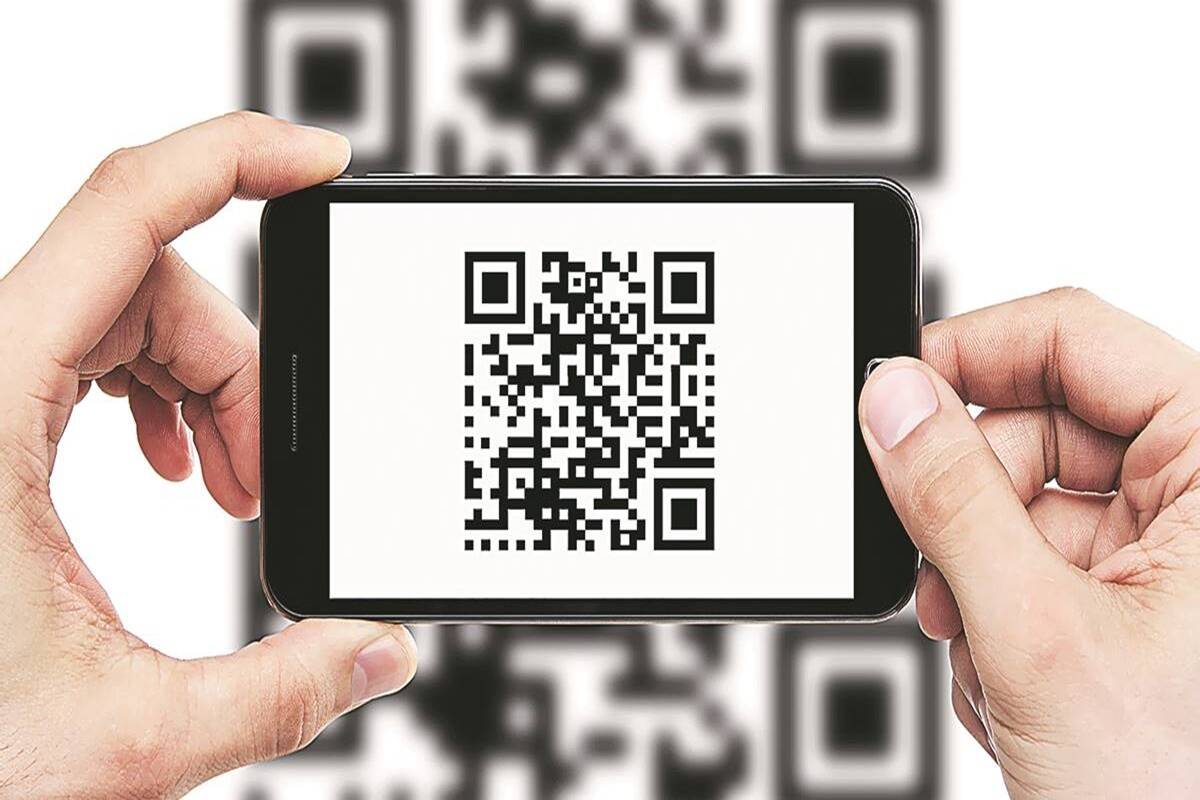
The black and white pixelated code in the shape of a square is known as a quick response code. These are simply secure lines of connection and communication between two individuals exchanging products, services and money.
Static QR-codes are commonly visible in merchant establishments and enable a contactless payment option to customers. Marketing billboards, restaurant menus and websites engage in the promotion of their products using quick response codes.
History of the QR-code
QR code is the brainchild of Masahiro Hara, a Japanese engineer who developed a standalone code to effectively track vehicles and equipment parts as they move through the manufacturing supply chain process.
A quick response code is also known as UPI scan code and is a modern variant of barcode which can be used in conjunction with smartphones. Information is stored in QR codes as a continuous series of pixels contained in a square grid which can be read in dual directions from right to left and top to bottom.
Technical Specs of QR-code
- With over 4000 characters, including special characters and punctuation, QR codes help encode data in HTTP addresses and phone numbers.
- During QR-code creation, data can be added, which enhances the code’s structural complexity and assists in personalization.
- Interestingly, the data structure in a QR-code is duplicated, which ensures that it can undergo scanner readability even when the code is damaged to the extent of thirty per cent.
Static QR code Vs UPI Scan codes
Design variations in QR codes are commonly based on function and encoded data. Primary categorization of QR code takes place in two ways: Static and UPI. Once created, the static QR-code cannot undergo further modification. This is quite an ideal scenario for generating a high volume of QR codes for a specific event.
A lack of creativity is evident in static scan code, for they are not in congruence with data analytics in computing the number of times the code has been scanned. The Wi-Fi password is a classic example of a good static QR-code.
Alternative Functions of QR-code
QR – codes can be used as a unique identifier of a product for tracking through the supply chain. They can also be used for:
- Social profile linking
- Menu navigation
- Downloading an app
- Boarding a flight
- Adding friends to a social media account
- Accessing Wi-Fi
- Sending and receiving payments
- Authenticating your login details
QR-codes offer limitless possibilities in how people conduct transactions and influence customers’ buying behaviour in the digital realm.
What are the different design variants of QR-code?
QR codes can be classified into four versions based on how data is stored and the mode of communication:
- The alphanumeric mode, which uses digits from 0 to 9 and special characters
- BYTE mode, which contains characters from the 8859 chipsets
- Numeric mode, which is by far the most effective mode of storing with up to 7000 characters
Conclusion
Thanks to some cutting-edge innovations in the QR-code design, they are now equipped with traceability function, anti-forgery measures, and enforce brand protection. All of these enhance the QR-code experience.